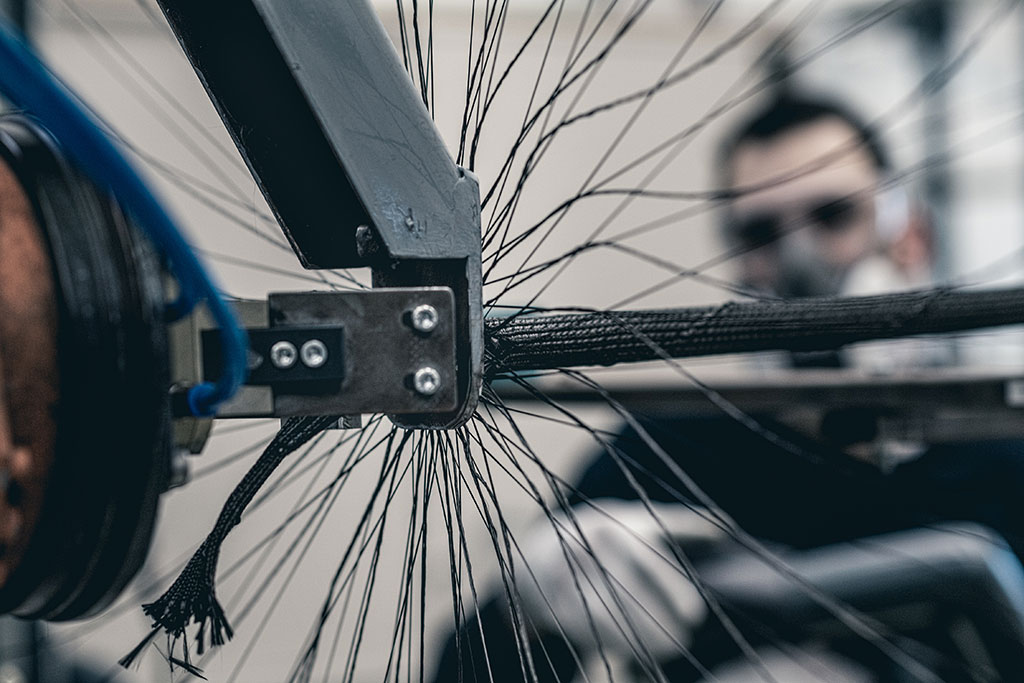
Braiding
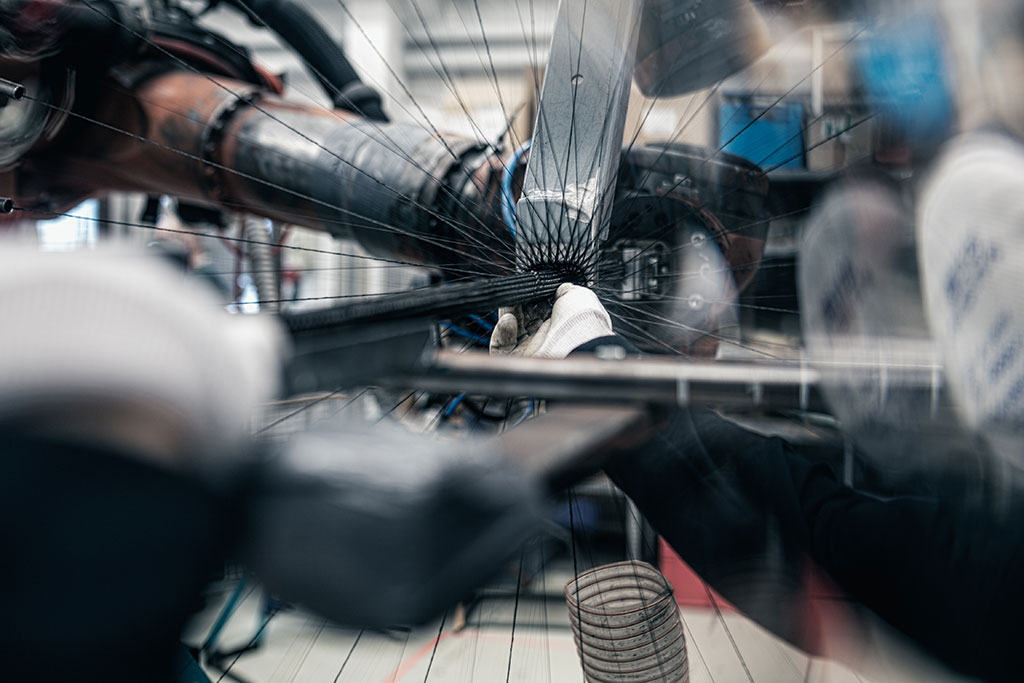
Carbon with its unique properties has long been known as the material of the future, but how does a carbon fiber become a rim? For carbon to become a reinforcement, the fibers must first be shaped. For this we use a high-speed radial braiding system. With their help, a braided reinforcement structure made of carbon fibers, the so-called preform. In this process step, the carbon fiber is braided around a forming core, which is later removed again to achieve maximum weight savings.
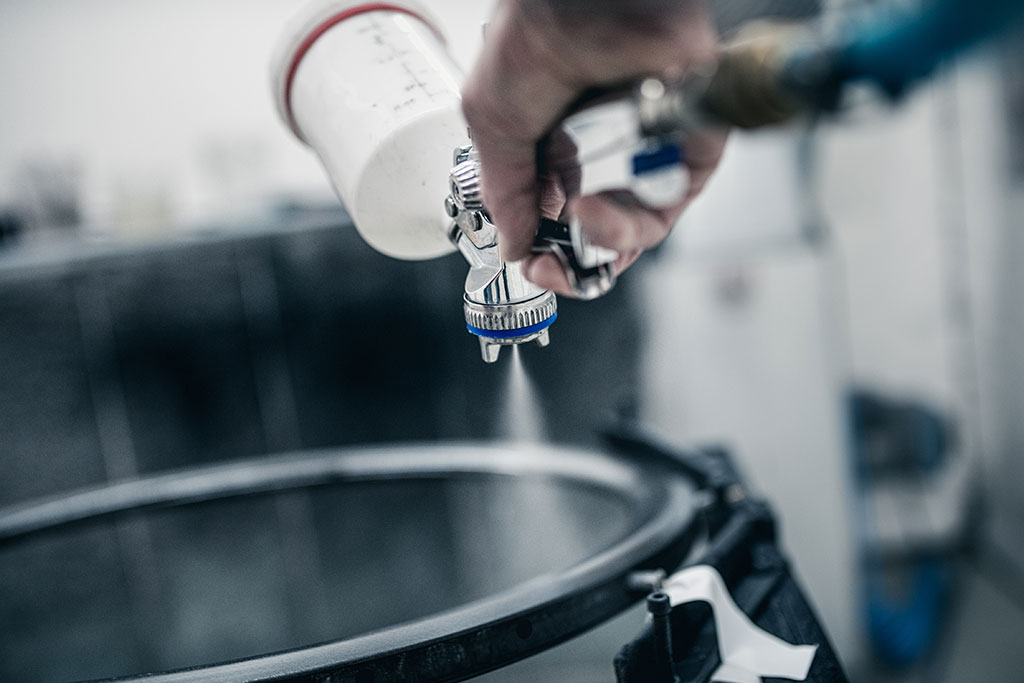
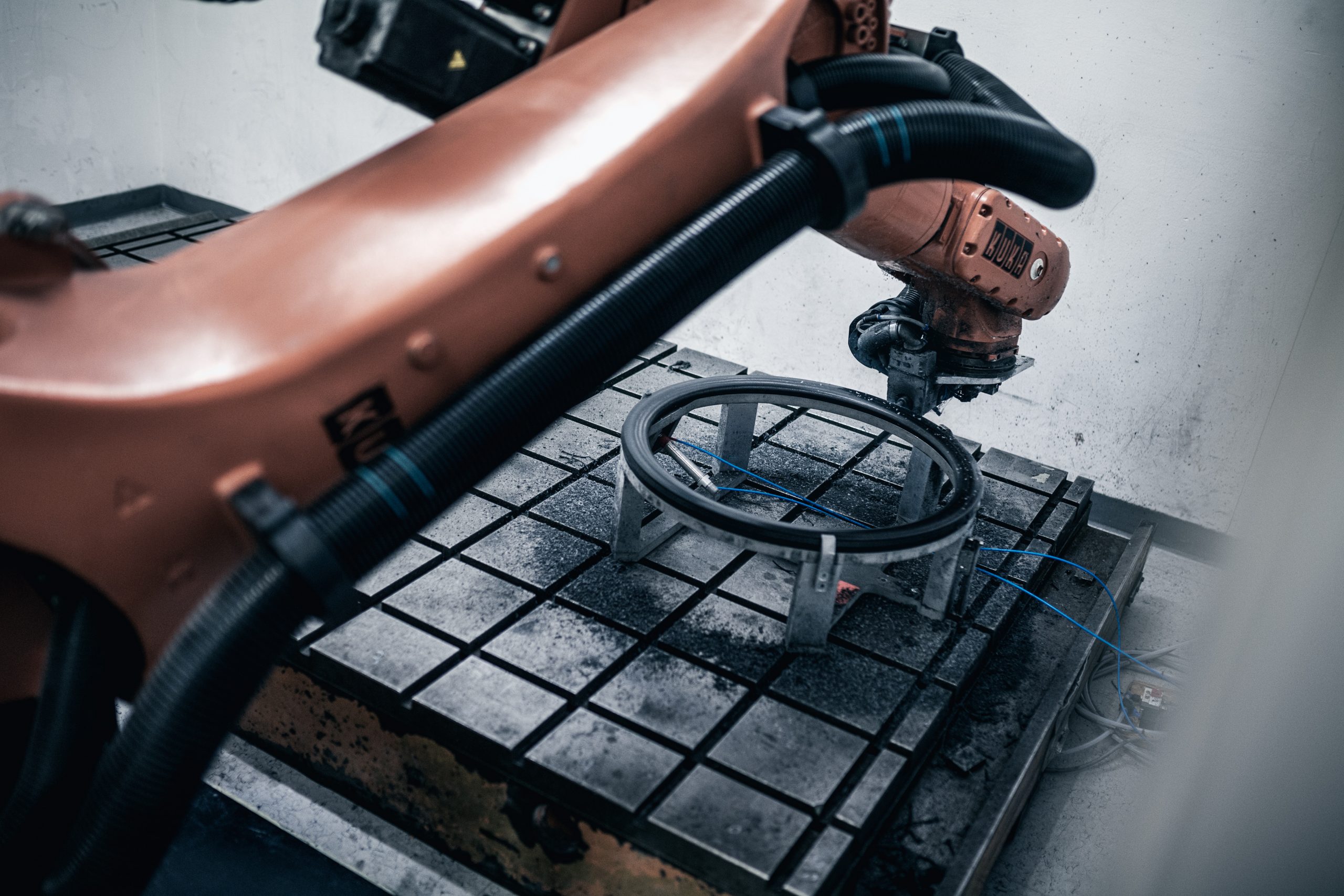
In the next step, the still “dry” textile, ie our preform, is injected with epoxy resin using the RTM process. In this injection process, the Resin Transfer Molding (RTM), the preform is placed in an aluminum mold specially manufactured for the respective component geometry and cured under pressure and temperature. At the end of this process step, we get the almost final rim, which now only has to be deburred and painted.
The advantage of this process is the possibility to maintain a constant quality level even with high quantities, thats why the automotive industry in particular uses this process for the production of CFRP components. Disadvantage again is that the investment costs for equipment and forms in this process are relatively high and thus often unsuitable for prototypes and small series.
What makes the difference?
We offer
- Unique, non-duplicable design through our UD braiding process
- Non-damaging fibers for best mechanical characteristics
- the reason why Airbus developed this braiding technique
- Not comparable to classic wicker wheels
- Aerospace technology: long, conducting research and development
Advantages of the machine braiding process
- No air pockets, as a continuous fiber is braided
- Machine production: do not lay a manual patch, thus no variances
- No overlaps
- Only a transition, since continuously wrapped
- No sanding of the transitions necessary
- Perfect resin distribution, as each fiber is uniformly enclosed by the resin
- Higher heat resistance
- No danger of delamination
- Higher security
- No carbon top layer – less weight
- Higher durability due to highest mechanical characteristics
 Deutsch
Deutsch